Difference between revisions of "NX8MMINI-D168"
From ICOP tech wiki
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td style="width:250px; padding:5px 25px 5px 25px;"> | <td style="width:250px; padding:5px 25px 5px 25px;"> | ||
| − | [[File:NX8Mmini-D168-FR2.png|alt=|frameless|連結=Special:FilePath/RIMG0272.JPG]]<blockquote>[[Media:NX8Mmini-D168-FR2.png|Click me for the raw pictures.]]</blockquote>[[File:Buy sample.png|center|frameless|125x125px|link= | + | [[File:NX8Mmini-D168-FR2.png|alt=|frameless|連結=Special:FilePath/RIMG0272.JPG]]<blockquote>[[Media:NX8Mmini-D168-FR2.png|Click me for the raw pictures.]]</blockquote>[[File:Buy sample.png|center|frameless|125x125px|link=https://www.icop-shop.com/product/nx8mm-d168-42cme/|alt=]]</td> |
<td style="padding:20px 30px 0px 0px; vertical-align:top; font-size:17px;"> | <td style="padding:20px 30px 0px 0px; vertical-align:top; font-size:17px;"> | ||
<h2> | <h2> | ||
Revision as of 17:06, 17 March 2022
| NX8MM-D168 |
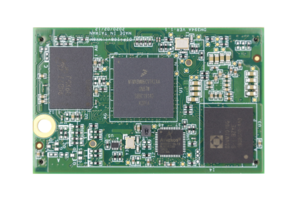 |
NX8MMINI-D168 IntroductionProviding an extremely small size board(35.00mm × 55.00mm), ICOP Technology launches a new ARM Cortex-A53 solution - NX8MMINI-D168. Equipping the NXP i.MX 8M Mini on ICOP’s unique DIP-168 module and provides an extensive I/O functions on board. The NX8MMINI-D168 provides I/O such as GPIO, UART, SD, DSI, CSI and High-quality audio based on S/PDIF or any interface based on SAI. For display, the IMX8MM-DIP168 supports up to 1080p encode and decode acceleration, 2D and 3D graphics.
|
| Specifications |
CPU |
NXP i.MX 8M Mini: Up to 4 × Cortex-A53 1.6GHz 1 × Cortex™-M4 |
Memory |
1/2/4 GB LPDDR4 |
GPU |
GC NanoUltra 3D (1 shader) GC320 2D OpenGL ES 2.0 |
Display |
MIPI-DSI up to 1080p60 |
Storage |
eMMC 16GB by default (up to 64GB) |
Network |
Ethernet: 10/100/1000 Mbps |
RTC |
On the carrier board |
I2C |
×4 |
SPI |
×3 |
UARTs |
×4 |
USB |
2 × USB 2.0 OTG, |
BUS |
PCIe |
Audio |
Headphone, |
Temperature Range |
0° to 60° C or -40° to 85° C (Optional) |
Dimensions |
35.00mm × 55.00mm |
| Yocto |
|
Sumo (kernel 4.14.98) Development |
| Android |
|
Pie 9.0 (kernel 4.14.98) Development |
